Warning: the performance of this simulation may vary from one system to another. Please see the description of the Extra Options Menu below for information on how to achieve the best performance on your computer.
Gnomon
General Description
This program simulates the shadow cast by a gnomon over the course of a day for any day of the year and any latitude on Earth. The program gives you the option to use mean Sun (which moves relative to the stars at a constant rate throughout the year) or true Sun (which varies its apparent speed relative to the background stars). The default is to use true Sun. The program also shows the observer's horizon plane on the spherical Earth, as well as the ecliptic and the apparent path of Sun. The Earth View can be set to let Earth rotate or remain fixed.
Gnomon Frame
- Gnomon Options Menu
- Pause After Each Day: if selected the simulation will automatically pause when time reaches 24 hours. If not selected the simulation will play continuously through to the next day.
- Use Mean Sun: if unchecked the simulation uses the true Sun, if checked the simulation uses the mean Sun.
- Trace Tip of Shadow: trace path drawn by tip of gnomon's shadow.
- Show North: show an arrow pointing North.
- Show Horizon Plane on Earth: show a view of the observer's horizon plane on a spherical Earth is a separate frame.
- Show Hourly Shadows: shows a sequence of shadows cast when time is equal to an integer number of hours. Shadows are not shown until the time they are cast and are lighter in color than the current shadow.
- Use Sundial: Selecting this option tilts the
gnomon so that it is aligned with Earth's rotational
axis (pointing toward the North Celestial Pole for
northern latitudes, toward the South Celestial Pole
for southern latitudes). At fixed latitude and
fixed time of day the direction of the shadow cast
by the mean sun is always the same in this configuration, regardless of the time of year (although the size of the shadow will change with time of year). Tilting the gnomon in this way thus makes it useful as a horizontal sundial.
- Select Special Day Menu: allows the user to set the day to one of the equinoxes or solstices.
- Extra Options Menu
- Connect Day Trace: connects the dots in the cyan trace of shadow's path while dragging the Day slider. You may need to use this option for this trace to be visible on some systems (ie Macs with Java 1.5). Note, however, that connecting the dots can sometimes cause spurious lines to be produced.
- Use Transparency While Running (only available when the simulation is paused): using transparency while running or dragging a slider drastically slows performance of this simulation on many systems, so the program is set to use no transparency while the surfaces are moving. However, on some systems (ie Macs with Java 1.5) the program performs well even with transparency on at all times. Select this option to test the performance of the simulation on your system.
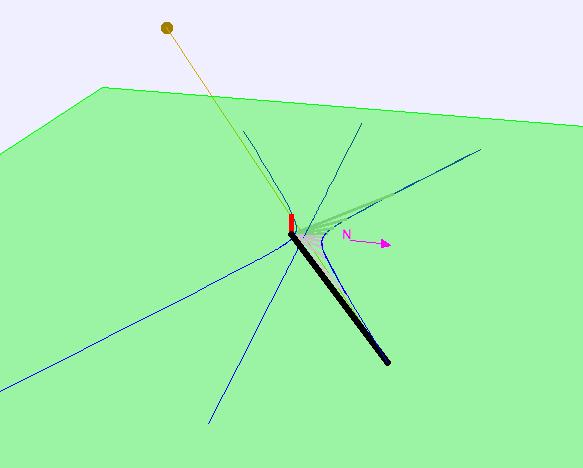
- Visual Elements
- Green plane: the horizon plane.
- Red line: the gnomon, which is aligned perpendicular to the horizon plane (ie vertical).
- Thick black/gray line: the shadow cast by the gnomon using the true sun (black) or mean sun (gray).
- Orange/green-gold sphere: true Sun (orange) or mean Sun (greenish gold).
- Blue trace: the path followed by the tip of the gnomon's shadow as time passes.
- Cyan trace: path followed by the tip of the gnomon's shadow at fixed time while the day is changed. This is useful for illustrating the analemma. To get a good trace drag the slider slowly. Note that some versions of Java (1.5.0_19) do not display this trace.
- Magneta arrow: points due North.
- Orange/green-gold line: line from true Sun (orange) or mean Sun (greenish gold) to top of gnomon to tip of shadow.
- Set of light gray lines: shadows cast when time is an integer number of hours.
- Controls
- Play/Pause: start and stop the simulation.
- Step: advance the simulation by one time step.
- Reset: reset simulation to original state.
- Clear Traces: clear all traces.
- Time: time of day, measured in hours from midnight. Mean Sun always reaches its greatest altitude at noon (hour 12).
- Day: day of the year, measured in days from the vernal equinox.
- Lat: latitude of gnomon's location on Earth, in degrees North. Use positive values for northern latitudes, negative values for southern latitudes.
Earth View Frame
- Earth View Options Menu
- Use Rotating Earth: let Earth rotate (while Sun remains fixed) as time passes. If not checked, Earth remains fixed and Sun moves around Earth.
- Show Sunbeam: show line from apparent location of Sun to tip of gnomon.
- Show Sun's Path: show a circle representing the apparent path of (mean) Sun.
- Show Ecliptic: show a circle representing the ecliptic.
- Show Horizon: show horizon plane.
- Show North Arrow: show arrow pointing north along horizon plane.
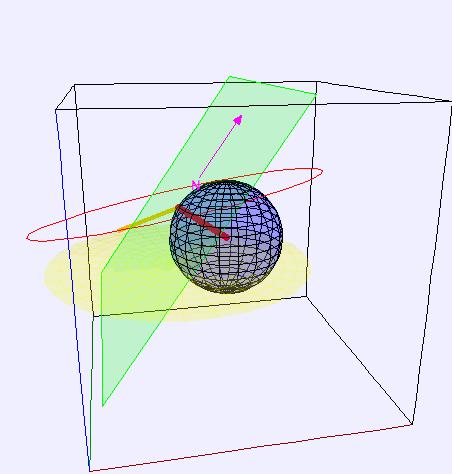
- Visual Elements
- Blue sphere: Earth.
- Green plane: the horizon plane.
- Red line: the gnomon, which is aligned perpendicular to the horizon plane (ie vertical).
- Thick orange line: sunbeam running from apparent location of mean Sun to tip of gnomon.
- Yellow circle: apparent path of mean Sun.
- Red circle: ecliptic.
- Magneta arrow: points due North.
- Controls
- Day: day of the year, measured in days from the vernal equinox.
- Lat: latitude of gnomon's location on Earth, in degrees North. Use positive values for northern latitudes, negative values for southern latitudes.
Version History
- Version 1.0 (7 Sep 2009): all of the basic functionality for the
vertical gnomon, work-arounds to address problems with slow 3D java
animation of transparent surfaces on some systems.
- Version 1.1 (5 Apr 2010): added option to tilt gnomon so that
it is aligned with Earth's rotational axis for use as a horizontal sundial.
Todd K. Timberlake (ttimberlake@berry.edu)



